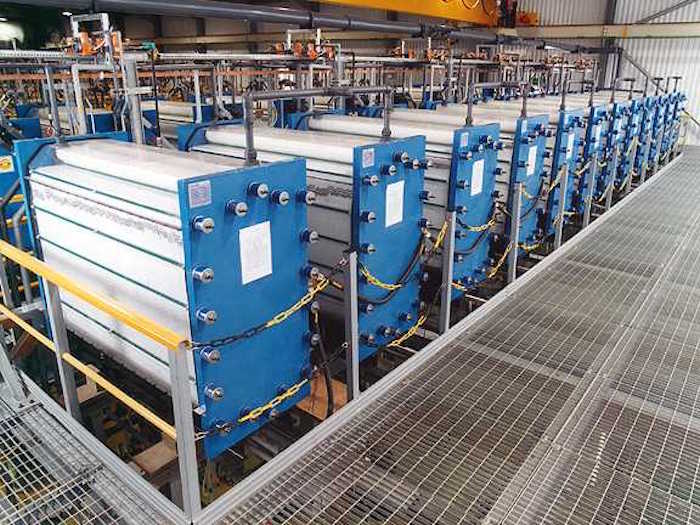

The Electrosynthesis Company has considerable experience developing energy storage technologies including electrochemical capacitors, batteries and regenerative fuel cells or redox flow batteries.
- Electrosynthesis formed a key part of the Research and Development group for Regenesys Technologies Ltd developing larger scale energy storage systems for use on the electricity grid. This technology was based on a polysulfide/bromide system.
- VRB Power Systems partnered with Electrosynthesis Company for the development of a Vanadium Redox Battery. This technology (currently being developed by Prudent Energy) is based on multiple stable valence states of vanadium.
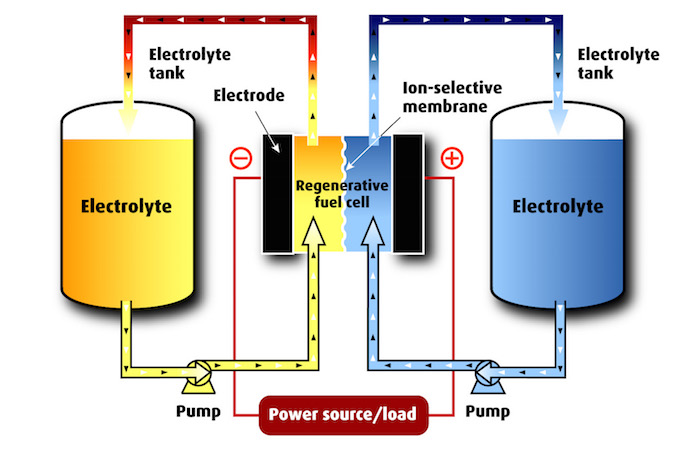
The redox flow battery is a form of rechargeable battery in which electrolyte containing one or more dissolved electroactive species flows through an electrochemical cell that, on charge, converts electricity into chemical energy. The electrolyte, and therefore energy, is stored externally in tanks until the energy is required when the solution is pumped back into the electrochemical cell discharging the chemical energy as electrical energy.
Advantages
- This is one of only a few technologies that can separate energy and power requirements. Power is determined by the size of the electrochemical cell whereas the energy is proportional to the size of the storage tanks.
- Large amounts of energy (up to hundreds of MWh) can be stored until required with little loss.
- High efficiency conversion from electrical to chemical energy
- Long cycle life with quick response times.
Applications
- Large (1 kWh – many MWh) stationary applications.
- Load leveling: store energy during times of low demand and provide electricity during peak time.
- Storing energy from renewable sources such as wind or solar to supply power during low generation periods.
- Uninterrupted power supply (UPS), to provide power when main power fails.
- Remote area power supplies (RAPS)
- Voltage support and frequency stabilization.